Gap Pad
Gap Pad
A complete range of choices for filling air gaps and enhancing thermal conductivity

The Bergquist company developed Gap Pad to meet the electronics industry’s growing need for interface materials with greater conformability, higher thermal performance and easier application. The Gap Pad family provides an effective thermal interface between heat sinks and electronic devices where uneven surface topography, air gaps and rough surface textures are present. Bergquist application specialists work closely with customers to specify the proper Gap Pad material for each unique thermal management requirement.

Each of the many products within the Gap Pad family is unique in its construction, properties and performance. Following is an overview of the important features offered by the Gap Pad family:
- Low-modulus polymer materials
- Available with fiberglass / rubber carriers or in a non-reinforced version
- Special fillers to achieve specific thermal and conformability characteristics
- Highly conformable to uneven and rough surfaces
- Electrically isolating
- Naturally tacky one-side or tacky on both sides with protective liner
- Variety of thicknesses and hardnesses
- Range of thermal conductivities
- Available in sheets and die-cut parts
Gap Pad thermal products are designed to improve an assembly’s thermal performance and reliability while saving time and money, specifically:
- Eliminates air gaps to reduce thermal resistance
- Highly conformability reduces interfacial resistance
- Low-stress vibration dampening
- Shock absorbing
- Easy material handling
- Simplified application
- Puncture, shear and tear resistance
- Improved performance for high-heat assemblies
- Compatible with automated dispensing equipment
Some Gap Pad products have special features for particular applications, including:
- Available with or without adhesive
- Rubber-coated fiberglass reinforcement
- Thicknesses from 0.010" to 0.250"
- Available in custom die-cut parts, sheets and rolls (converted or unconverted)
- Custom thicknesses and constructions
- Adhesive or natural inherent tack
Gap Pad® materials are highly conformable, thermally conductive interface pads designed to fill air gaps between heat-generating components and heat spreaders, helping improve cooling performance across multiple applications. Available in various thicknesses and custom shapes with or without adhesive, Gap Pads support consistent thermal management even when component heights differ.
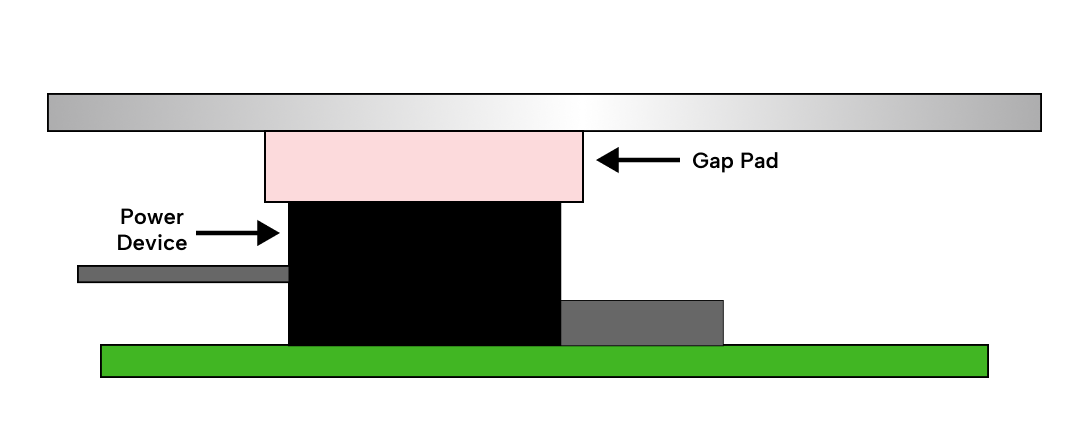
- Between an IC and a heat sink or chassis. Typical packages include BGA's, QFP, SMT power components and magnetics
- Between a semiconductor and heat sink
- CD-Rom/DVD cooling
- Between heat generating devices and chassis
- Heat pipe assemblies
- RDRAM memory modules
- Hard Drive cooling
- Power supply
- Signal amplifiers
SUPPORT FAQs
Common Questions About Our Products
What thermal conductivity test method was used to achieve the values given on the data sheet?
A test fixture is utilised that meets the specifications outlined in ASTM D5470
Is Gap Pad offered with an adhesive?
Currently, Gap Pad VO, Gap Pad VO Soft and Gap Pad VO Ultra Soft are offered with or without an adhesive on the Sil-Pad 800/900 carrier-side of the material. The remaining surface has natural inherent tack. All other Gap Pads have inherent tack.
Is the adhesive repositionable?
Depending on the surface being applied to, if care is taken, the pad may be repositioned. Special care should be taken when removing the pad from aluminum or anodised surfaces to avoid tearing or delamination.
What is meant by natural tack?
The characteristic of the rubber itself has a natural inherent tack, without the addition of an adhesive. As with adhesive-backed products, the surfaces with natural tack may help in the assembly process to temporarily hold the pad in place while the application is being assembled. Unlike adhesive-backed products, inherent tack does not have a thermal penalty since rubber itself has the tack. Tack strength varies from one Gap Pad product to the next.
Can Gap Pad with natural tack be repositioned?
Again, depending on the material that the pad is applied to, in most cases they are repositionable. Care should be taken when removing the pad from aluminum or anodised surfaces as to avoid tearing or delaminating the pad. The side with natural tack is always easier to reposition than an adhesive side.
Is Gap Pad reworkable?
Depending on the application and the pad being used, Gap Pad has been reworked in the past. Bergquist has customers that are currently using the same pad for reassembling their applications after burn-in processes and after fieldwork repairs. However, this is left up to the design engineer’s judgment as to whether or not the Gap Pad will withstand reuse.
Is liquid Gap Filler reworkable?
It is highly dependent on the application and its surface topography. Liquid Gap Filler will cure with low adhesive strength to the application surfaces.
Will heat make the material softer?
From -60°C to 200°C, there is no significant variance in hardness for silicone Gap Pads and Gap Fillers.
What is the shelf life of Gap Pad?
Shelf life for Gap Pad is one (1) year after date of manufacture. For Gap Pad with adhesive, the shelf live is (6) six months after the date of manufacture. After these dates, inherent tack and adhesive properties should be recharacterised.
How is extraction testing performed?
The test method used is the Bellcore Extraction method #TR-NWT-000930; refer to Bergquist Application Note #56.
What are the upper processing temperature limits for Gap Pad and for how long can Gap Pad be exposed to them?
Gap Pad VO materials and Gap Pad A3000 are more stable at elevated temperatures. Gap Pad in general can be exposed to temporary processing temperatures of 250°C for five minutes and 300°C for one minute.
Is Gap Pad electrically isolating?
Yes, all Gap Pad materials are electrically isolating. However, keep in mind that Gap Pad is designed to FILL gaps and is not recommended for applications where high mounting pressure is exerted on the Gap Pad.
How much force will the pad place on my device?
Refer to the Pressure vs. Deflection chart in Bergquist Application Note #116.
Will Gap Pad and Gap Filler work in my application? What size gaps will Gap Pad and Gap Filler accommodate?
Gap Pad and Gap Filler can be used wherever air can be replaced, such as between a heat-generating device and a heat sink, heat spreader or housing. This can be done using one sheet of Gap Pad or individual pieces of appropriate thicknesses, or by using Gap Filler if stack-up tolerances and height variations are significant.
What is meant by "compliance" and "conformability", and why is this important?
The better a Gap Pad complies and conforms to a rough or stepped surface, the less interfacial resistance will be present due to air voids and air gaps. This leads to a lower overall thermal resistance of the pad between the two interfaces.
Is anything given off be the material (e.g. extractables, outgassing)?
1) Silicon Gap pad and Gap Fillers, like all soft silicone materials, can extract silicone fluid (refer to Bergquist Application Note #56). Also note that Gap Pad and Gap Filler have some of the lowest extraction values for silicone-based gap filling products on the market and if your application requires no silicone, see our line of Sil-Free material.
2) Primarily for aerospace applications, outgassing data is detailed in Bergquist Application Note #117, tested per ASTM E595
Why does the data sheet describe the hardness rating as a bulk rubber hardness?
A reinforcement carrier is generally utilized in Bergquist Gap Pads for ease of handling. When testing hardness, the reinforcement carrier can alter the test results and incorrectly depict thinner materials as being harder. To eliminate this error, a 250mil rubber puck is molded with no reinforcement carrier. The puck is then tested for hardness. The Shore hardness is recorded after a 30 second delay.
Need More Help?
Let’s Solve Your Thermal Challenges Together
Get expert support for product selection, datasheets, and engineering guidance tailored to your application needs.

